What is Structured Query Language?
As a data engineer, you can interact with databases using Structured Query Language or as it’s more commonly known, SQL, also pronounced as sequel.
Interactions with database
- Create
- Read
- Update
- Delete
These operations are also known as CRUD operations.
SQL
SQL
SQL is the standard language that can be used with all databases. It’s particularly useful when working with relational databases, which require a language that can interact with structured data.
Some examples of relational databases that SQL can interact with include:
- MySQL
- PostgreSQL
- Oracle
- Microsoft SQL Server
Interpret or read and execute instructions given using SQL
A database interprets and make sense of SQL instructions with the use of a Database Management System or DBMS.
As a web developer, you’ll execute all SQL instructions on a database using a DBMS. The DBMS takes responsibility for transforming SQL instructions into a form that’s understood by the underlying database.
SQL usage
Performing CRUD operations is the most common task when working with the database. CRUD stands for create read update and delete. Or in operational terms, create, add or insert data, read data, update existing data and delete data alongside these operations.
SQL subsets
There are many other things that SQL can do. Depending on what SQL is used for, it can be divided into many subsections or sub languages.
- DDL : data definition language
- DML : data manipulation language
- DQL : data query language
- DCL : called data control language
DDL
DDL as the name says helps you define data in your database.
Before you can store data in the database. You need to create the database and related objects like tables in which your data will be stored. For this, the DDL part of SQL has a command named create.
Then you might need to modify already created database objects. For example, you might need to modify the structure of a table by adding a new column. You can perform this task with the DDL alter command.
You can remove an object like a table from a database using the DDL drop command.
DML
Data manipulation language or DML commands are used to manipulate data in the database, like inserting updating or deleting data. Most crude operations fall under DML.
To add data to a table, you can use the insert command. This command lets you specify the fields to add data too, along with the values to be inserted.
If you need to edit data that’s already inserted into a table, just deploy the update command.
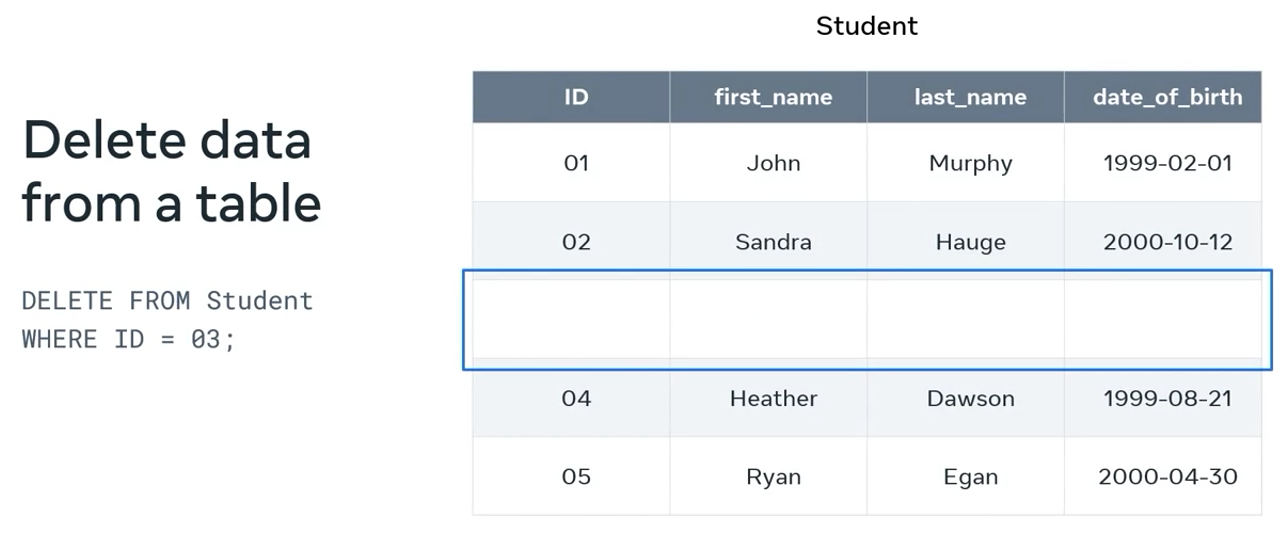
And you can specify data to be removed by using the delete command.
DQL
To read data stored in a database, you can use data query language.
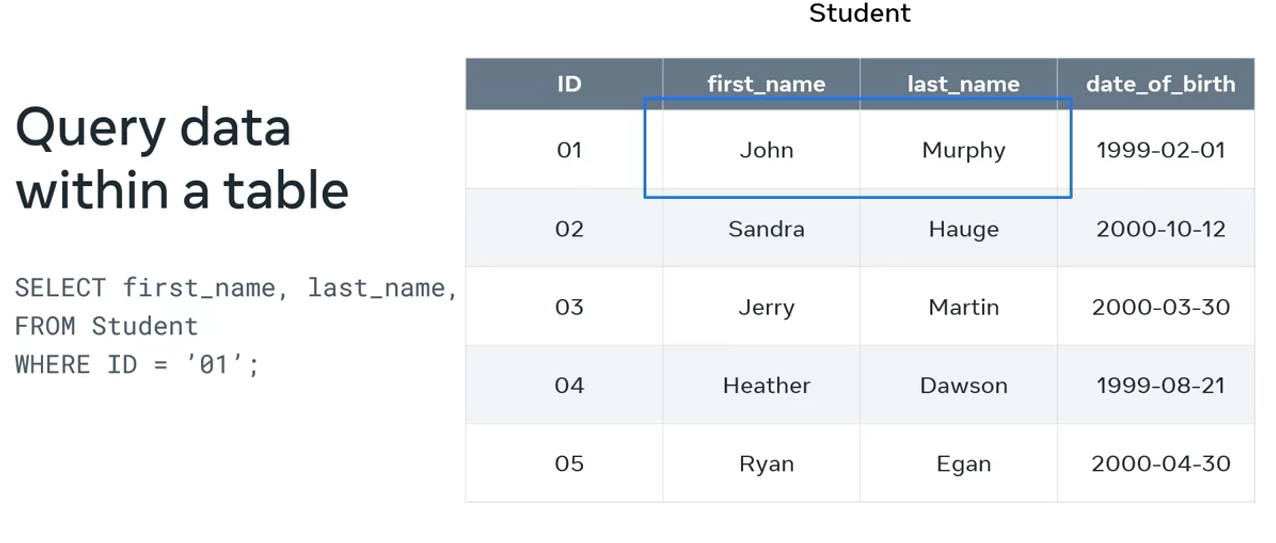
DQL defines a select command to be able to retrieve data. Select lets you retrieve data from one or multiple tables letting you specify the data fields that you want based on preferred filter criteria.
DCL
You can also use DCL or data control language to control access to the database.
For example, using DCL commands, you control access to data stored in the database. Grant and revoke DDL commands are used to give users access privileges to data, and to revert access privileges already given to users.
Advantages of SQL
SQL is the interface or bridge between a relational database and its users and offers web developers a wide range of advantages.
Requires less skills
The biggest advantage of SQL is that it requires very little coding skills to use, is just a set of keywords. There aren’t many lines of code required to perform basic CRUD operations, or add, create, update, and delete tasks on the database. It’s a very developer or user-friendly language.
SQL’s interactivity makes it even more user-friendly because it lets developers write complex queries in a short space of time. If you need to work with relational databases for your next project, you just need to know what keywords to use and when.
Works with all relational databases
SQL is also a standard language that can be used with all relational databases like MySQL. This also means that there’s a lot of support and information available. SQL can run on any computer once you’ve database software installed.
Portable
SQL is also a portable language.Once you write your code, it can then be used in any hardware, on any operating system or platform wherever you need. If you write SQL code in a desktop and then move it to a production server environment, it will run the same in both locations.
Covers all the needs
Also, SQL is a comprehensive language that covers all areas of database management administration.
For example, it allows you to create databases, insert, update, and delete data, retrieve and share data among multiple users and manage database security.
TIP
This is made possible through subsets of SQL like DDL or Data Definition Language, DML, also known as Data Manipulation Language, DQL or Data Query Language, and DCL, also known as Data Control Language.
Large data
The final advantage of SQL is that it lets database users process large amounts of data quickly and efficiently.
SQL syntax introduction
Create database
The first task is to create the database. To do this, I already create statement using SQL DDL subset.
CREATE DATABASE database_name;Create tables
CREATE TABLE table_name;Populate the table
This is where I can use the data manipulation language or DML subset of SQL. To add table data, I use the insert into syntax. This inserts rows of data into a given table.
I just type insert into, followed by the table name, and then a list of required columns or fields within a pair of parentheses. Then I add the values keyword and specify in order the values for each of the fields.
INSERT INTO table_name
(column_one, column two,
column three...)
VALUES (value1, value2,
value3, ...);
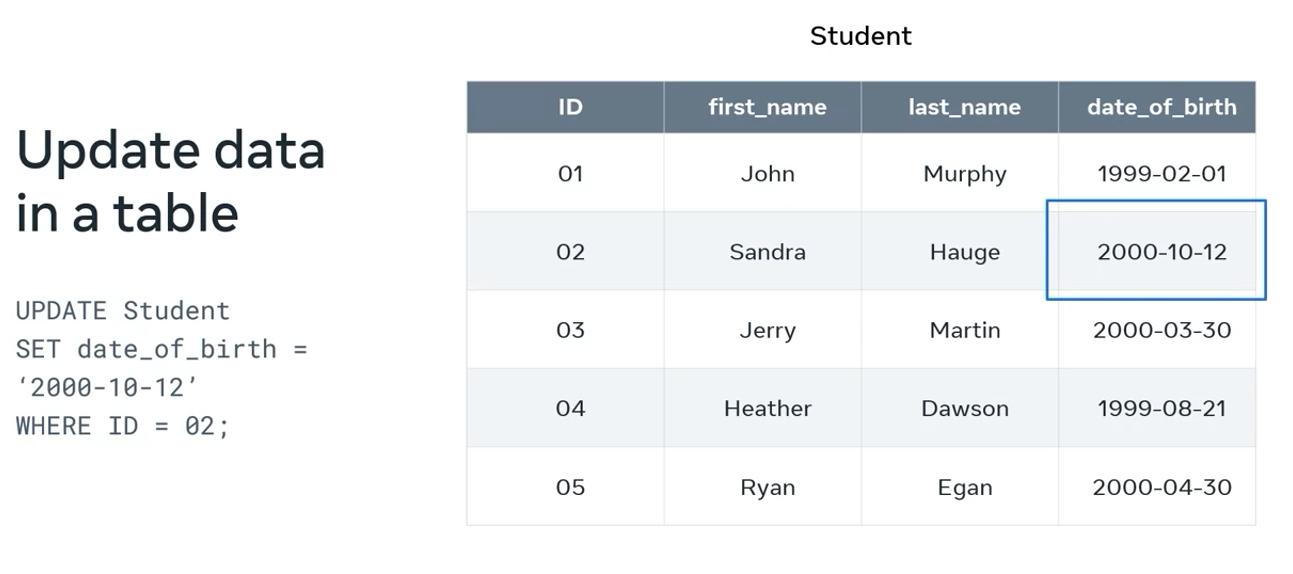
Update or modify data
To change this data, I can use the update syntax, which is part of the DML subset of SQL.
Deleting data
Reading data
That’s where SQL, DQL or data query language comes in. The main syntax of DQL is select.
Common SQL Commands
The objective of this reading is to teach you how to name and explain the main commands in SQL. SQL is the most widely used database query language. It is designed for retrieving and managing data in a relational database. SQL can be used to perform different types of operations in the database such as accessing data, describing data, manipulating data and setting users roles and privileges (permissions).
Here you will learn about the main commands used in SQL. At a later stage you will explore relevant examples of how to use these commands with a detailed explanation of the SQL syntax for key operations such as to create, insert, update and delete data in the database.
The SQL Commands are grouped into four categories known as DDL, DML, DCL and TCL depending on their functionality, namely the type of operation they’re used to perform. Let’s explore these commands in greater detail.
Data Definition Language (DDL)
The SQL DDL category provides commands for defining, deleting and modifying tables in a database. Use the following commands in this category.
CREATE Command
Purpose: To create the database or tables inside the database
Syntax to create a table with three columns:
CREATE TABLE table_name (column_name1 datatype(size), column_name2 datatype(size), column_name3 datatype(size));DROP Command
Purpose: To delete a database or a table inside the database.
Syntax to drop a table:
DROP TABLE table_name;ALTER Command
Purpose: To change the structure of the tables in the database such as changing the name of a table, adding a primary key to a table, or adding or deleting a column in a table.
- Syntax to add a column into a table:
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD (column_name datatype(size));- Syntax to add a primary key to a table:
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD primary key (column_name);TRUNCATE Command
Purpose: To remove all records from a table, which will empty the table but not delete the table itself.
Syntax to truncate a table:
TRUNCATE TABLE table_name;COMMENT Command
Purpose: To add comments to explain or document SQL statements by using double dash (—) at the start of the line. Any text after the double dash will not be executed as part of the SQL statement. These comments are not there to build the database. They are only for your own use.
Syntax to COMMENT a line in SQL:
--Retrieve all data from a table
SELECT * FROM table_name; Data Query Language (DQL)
The SQL DQL commands provide the ability to query and retrieve data from the database. Use the following command in this category.
SELECT Command
Purpose: To retrieve data from tables in the database.
Syntax to select data from a table:
SELECT * FROM table_name;Data Manipulation Language (DML)
The SQL DML commands provide the ability to query, delete and update data in the database. Use the following commands in this category.
INSERT Command
Purpose: To add records of data into an existing table. Syntax to insert data into three columns in a table:
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, column3) VALUES (value1, value2, value3);UPDATE Command
Purpose: To modify or update data contained within a table in the database.
Syntax to update data in two columns:
UPDATE table_name SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2 WHERE condition;DELETE Command
Purpose: To delete data from a table in the database.
Syntax to delete data:
DELETE FROM table_name WHERE condition;Data Control Language (DCL)
You use DCL to deal with the rights and permissions of users of a database system. You can execute SQL commands to perform different types of operations such as create and drop tables. To do this, you need to have user rights set up. This is called user privileges. This category deals with advanced functions or operations in the database. Note that this category can have a generic description of the two main commands. Use the following commands in this category:
GRANT Command to provide the user of the database with the privileges required to allow users to access and manipulate the database.
REVOKE Command to remove permissions from any user.
Transaction Control Language (TCL)
The TCL commands are used to manage transactions in the database. These are used to manage the changes made to the data in a table by utilizing the DML commands. It also allows SQL statements to be grouped together into logical transactions. This category deals with advanced functions or operations in a database. Note that this category can have a generic description of the two main commands. Use the following commands in this category:
COMMIT Command to save all the work you have already done in the database.
ROLLBACK Command to restore a database to the last committed state.
Additional resources
The following resources are some additional reading material that introduces you to SQL. These will enable you to enhance your knowledge on SQL syntaxes and common SQL commands (DQL, DML and DDL) that you’ve learned throughout this lesson.
Previous one → 1.Databases and data | Next one → 3.Basic database structure